Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fukaya, Yuki
Hyomen Kagaku, 37(11), p.547 - 552, 2016/11
no abstracts in English
 7 surface reconstruction
7 surface reconstructionAsaoka, Hidehito; Uozumi, Yuki
Hyomen Kagaku, 37(9), p.446 - 450, 2016/09
no abstracts in English
 (110)(1
(110)(1 2) surface using total-reflection high-energy positron diffraction (TRHEPD)
2) surface using total-reflection high-energy positron diffraction (TRHEPD)Mochizuki, Izumi*; Ariga, Hiroko*; Fukaya, Yuki; Wada, Ken*; Maekawa, Masaki*; Kawasuso, Atsuo*; Shidara, Tetsuo*; Asakura, Kiyotaka*; Hyodo, Toshio*
Hyomen Kagaku, 37(9), p.451 - 456, 2016/09
no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Tomokazu*; Kishi, Hirofumi*; Yamaguchi, Susumu*; Tanaka, Hirohisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Nishihata, Yasuo
Hyomen Kagaku, 37(2), p.78 - 83, 2016/02
We have developed direct liquid fuel anion exchange membrane fuel cell vehicles to deal with the global warming. Non-platinum group metals (PGM) catalyst has been researched to apply for both anode and cathode electrodes. A test driving was carried out for the fuel cell vehicle equipped with no precious metals as catalysts at SPring-8 in 2013. Here we introduce our results of advanced analysis for reaction mechanism and active site of non-PGM catalyst using synchrotron radiation X-rays at SPring-8.
Kanno, Ryoji*; Hirayama, Masaaki*; Suzuki, Kota*; Tamura, Kazuhisa
Hyomen Kagaku, 37(2), p.52 - 59, 2016/02
Batteries are a key technology in today's society. Since the lithium-ion configuration has been widely accepted, significant efforts have been devoted to attain high energy and power densities to produce an excellent energy storage system without any safety issue. To improve the reliability and power characteristics of batteries, deep insights into the reactions at the electrode/electrolyte interface are necessary. The model systems with epitaxial thin-film electrodes might be suitable for understanding these reactions. The in situ techniques for directly observing surface structural changes of the electrodes have been developed for surface X-ray scattering and neutron reflectivity techniques. These techniques are reviewed and future studies on the interfacial reaction in batteries will be discussed.
Ikeda, Takashi; Hou, Z.*; Chai, G.-L.*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*
Hyomen Kagaku, 36(7), p.345 - 350, 2015/07
Carbon alloy catalysts (CACs) are one of promising candidates for platinum-substitute cathode catalysts for polymer electrolyte fuel cells. We have investigated possible mechanisms of oxygen reduction reactions (ORRs) for CACs via first-principles-based molecular dynamics simulations. In this contribution, we review possible ORRs at likely catalytic sites of CACs suggested from our simulations.
Terauchi, Masami*; Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato
Hyomen Kagaku, 36(4), p.184 - 188, 2015/04
Electron beam induced soft-X-ray emission spectroscopy (SXES) that uses a grating spectrometer has been introduced to a conventional scanning electron microscope (SEM) for characterizing desired specimen areas of bulk materials. The spectrometer has a grazing-incidence flat-field optics by using aberration corrected (varied-line-spacing) gratings, which has already been applied to transmission electron microscopes. The best resolution was confirmed as 0.13 eV at Mg L-emission (50 eV), which is comparable with that of recent dedicated electron energy-loss spectroscopy instruments. Apparent band structure effects have been observed in Mg-L, Si-L, B-K, and Ti-L emission spectra obtained from bulk materials using SEM-SXES instrument.
Onuki, Kaoru; Noguchi, Hiroki; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Kubo, Shinji
Hyomen Kagaku, 36(2), p.80 - 85, 2015/02
Thermochemical water-splitting process decomposes water using thermal energy by operating high temperature endothermic reaction(s) and low temperature exothermic reaction(s) cyclically, with which free energy of water decomposition is produced. The so-called sulfur family processes, which utilize thermal decomposition of sulfuric acid as the high temperature endothermic reaction, have attracted lots of interest among the many processes proposed so far. The IS process represents the pure thermochemical sulfur family processes. The continuous hydrogen production by IS process was demonstrated in laboratory, and the materials of construction for the IS process have been screened by corrosion tests performed in the severe process environment. At present, application of membrane technologies and development of catalysts are under study to improve the hydrogen production performance. Also, development is underway of the chemical reactors made of candidate materials such as ceramics.
Esaka, Fumitaka; Magara, Masaaki; Suzuki, Daisuke; Miyamoto, Yutaka; Kimura, Takaumi
Hyomen Kagaku, 34(3), p.125 - 130, 2013/03
Analysis of individual particles containing nuclear materials in environmental samples gives important information on the origins. This paper describes analytical techniques of individual particles containing nuclear materials such as uranium and plutonium. A scanning electron microscope (SEM) combined with an X-ray detector, solid track detectors, and secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) were used to identify particles containing uranium and/or plutonium in environmental samples. Isotope ratios for these particles were successfully determined with SIMS, thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS) or inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICPMS). The complementary use of these methods is effective to characterize individual particles rapidly, precisely and accurately.
Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Hyomen Kagaku, 34(3), p.135 - 142, 2013/03
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Hiroshi*; Teraoka, Yuden
Dai-54-Kai Hyomen Kagaku Kiso Koza; Hyomen, Kaimen Bunseki No Kiso To Oyo Tekisuto, p.109 - 128, 2012/10
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Masamitsu
Hyomen Kagaku, 33(9), p.507 - 512, 2012/09
Surface structures of GaAs(001) under growth conditions have been investigated using in situ X-ray diffraction. The atomic arrangements of GaAs(001) surface stabilized at an elevated temperature under as pressure were quantitatively determined in a molecular-beam epitaxy chamber integrated with an X-ray diffractometer. With the help of high angular resolution of synchrotron radiation, disordered structures appearing in the transition from (2 4) to other phases were clarified. Energy tunability of synchrotron X-rays allowed for element-specific analysis of the c(4
4) to other phases were clarified. Energy tunability of synchrotron X-rays allowed for element-specific analysis of the c(4 4) structure, providing direct evidence for Ga-As heterodimer formation.
4) structure, providing direct evidence for Ga-As heterodimer formation.
Tamura, Kazuhisa
Hyomen Kagaku, 33(9), p.524 - 529, 2012/09
Electrochemical reaction is one of the reactions which occur at solid/liquid interfaces. In the last three decades, relationships between reactivity and structure of solid/liquid interface, especially, electrode surface structure were uncovered using various techniques. Thus, nowadays it has been well recognized the importance of the study of electrode surface structures in in situ condition. However, dynamics of electrode surface structure has been well uncovered. Surface X-ray scattering (SXS) is one of the in situ techniques which can be applied to the study of the solid/liquid interface structures. One of the advantages of SXS is that measurements can be carried out under ideal electrochemical conditions. In this review, dynamics in underpotential deposition process of Bi on Au(111) electrode studied using surface X-ray scattering will be reported.
Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yamada, Takatoshi*; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Watanabe, Daiki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hasegawa, Masataka*; Teraoka, Yuden; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Hyomen Kagaku, 33(8), p.449 - 454, 2012/08
Graphene-on-insulator structures are required for fabrication of the graphene transistor. Diamond has been attracted as the substrate for graphene growth because it has a larger band gap and break down voltage compared with SiC. The detail of graphitization on a diamond surface has not been clarified yet because the nondestructive evaluation for graphene-on-diamond (GOD) structure was hard. In this study, we have developed an evaluation method of GOD based on the photoemission spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation focusing the shift of photoelectron spectra due to band bending. We can clearly determine the graphitization temperature on the diamond C(111) surface as approximately 1120 K, which is lower than that on an SiC substrate. It is also confirmed from C 1s photoelectron spectra, there is the buffer layer at the interface between the grapheme layer and the diamond substrate.
 7 surface using O
7 surface using O at 300 K and those formation processes observed by real-time synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
at 300 K and those formation processes observed by real-time synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyYoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
Hyomen Kagaku, 33(3), p.172 - 177, 2012/03
To understand reaction mechanism of the oxidation at an Si(111)-7 7 surface using O
7 surface using O at 300 K, the determination of initial products is essentially important. Oxygen bonding configurations and silicon oxidation states were observed using real-time X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy for O1s together with Si 2p. It is found that
at 300 K, the determination of initial products is essentially important. Oxygen bonding configurations and silicon oxidation states were observed using real-time X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy for O1s together with Si 2p. It is found that 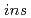 structure initially forms, where one oxygen atom inserts in the backbond of Si adatom. It is ascertained that the chemisorbed molecular oxygen, so-called
structure initially forms, where one oxygen atom inserts in the backbond of Si adatom. It is ascertained that the chemisorbed molecular oxygen, so-called  oxygen, is the adsorbate on top of the
oxygen, is the adsorbate on top of the 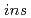 structure. It is also clarified that
structure. It is also clarified that  -
-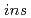 structure and
structure and 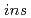 -
-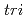 structure, where
structure, where 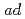 means an oxygen atom on top of Si atom and
means an oxygen atom on top of Si atom and 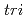 means the interstitial oxygen atom, appear after a short time. Our results imply the presence of a mobile O
means the interstitial oxygen atom, appear after a short time. Our results imply the presence of a mobile O on the surface.
on the surface.
Yamazaki, Tatsuya; Yamazaki, Dai; Asaoka, Hidehito; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Shamoto, Shinichi; Toyoshima, Yasutake*
Hyomen Kagaku, 31(8), p.380 - 385, 2010/08
Strontium (Sr) is a well-known template on Si for a highly-desirable transistor gate material SrTiO . Sr layers are grown epitaxially on hydrogen-terminated Si(111) surface despite the large lattice mismatch of 12%. However, there are still many unclear points concerning the specific interface structure. We need to study how the buried monatomic hydrogen layer behaves to manage the large mismatch. In order to clarify its buried hetero-interface structure related to monatomic hydrogen layer, Si-H bonding states are in situ monitored during Sr growth by Multiple Internal Reflection Fourier Transform Infrared (MIR-FTIR) spectroscopy, and the buried hetero-interface between Sr layer and Si(111) surface is investigated by ex situ neutron reflectometry (NR). FTIR has shown change of Si-H bonding states caused by the Sr growth at the initial monolayer growth stage. Furthermore, we have found the difference in neutron reflectivity profiles between the Sr layers grown on H- and D-terminated Si substrates. These results suggest the existence of buried monatomic hydrogen layer at the hetero-interface acting as an effective component of interface structure to manage the high lattice mismatch.
. Sr layers are grown epitaxially on hydrogen-terminated Si(111) surface despite the large lattice mismatch of 12%. However, there are still many unclear points concerning the specific interface structure. We need to study how the buried monatomic hydrogen layer behaves to manage the large mismatch. In order to clarify its buried hetero-interface structure related to monatomic hydrogen layer, Si-H bonding states are in situ monitored during Sr growth by Multiple Internal Reflection Fourier Transform Infrared (MIR-FTIR) spectroscopy, and the buried hetero-interface between Sr layer and Si(111) surface is investigated by ex situ neutron reflectometry (NR). FTIR has shown change of Si-H bonding states caused by the Sr growth at the initial monolayer growth stage. Furthermore, we have found the difference in neutron reflectivity profiles between the Sr layers grown on H- and D-terminated Si substrates. These results suggest the existence of buried monatomic hydrogen layer at the hetero-interface acting as an effective component of interface structure to manage the high lattice mismatch.
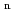 H
H (n
(n 2) molecules from adsorbed methane by low-energy ion irradiation
2) molecules from adsorbed methane by low-energy ion irradiationNarita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Hyomen Kagaku, 29(8), p.489 - 494, 2008/08
The formation of molecular ions and neutral molecules from adsorbed CH , CD
, CD and N
and N following 1 keV He
following 1 keV He ion irradiation has been investigated. The thickness of the adsorbed layer was precisely controlled. For mono-layered methane, only monomer ions (CH
ion irradiation has been investigated. The thickness of the adsorbed layer was precisely controlled. For mono-layered methane, only monomer ions (CH
 ) were desorbed, while a large number of heavy ions (C
) were desorbed, while a large number of heavy ions (C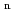 H
H
 ) up to n = 20 as well as heavy neutral molecules (C
) up to n = 20 as well as heavy neutral molecules (C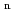 H
H ) were desorbed from multi-layered film. Among the desorbed ions and neutral molecules, molecules with C-C covalent bonds such as acetylene and ethylene were found. The results indicate that chemical bonds are newly formed by ion irradiation. Based on the results for thickness dependences of the mass spectra and calculation of He
) were desorbed from multi-layered film. Among the desorbed ions and neutral molecules, molecules with C-C covalent bonds such as acetylene and ethylene were found. The results indicate that chemical bonds are newly formed by ion irradiation. Based on the results for thickness dependences of the mass spectra and calculation of He energy loss process from TRIM-Code, it was elucidated that the monomer ions are desorbed from the top surface layer through single electron excitation. On the other hand, the cluster ions are formed mainly in the inside of the layers along the nuclear track due to phonon excitation, which is produced by nuclear collision between incident He
energy loss process from TRIM-Code, it was elucidated that the monomer ions are desorbed from the top surface layer through single electron excitation. On the other hand, the cluster ions are formed mainly in the inside of the layers along the nuclear track due to phonon excitation, which is produced by nuclear collision between incident He ions and adsorbed molecules.
ions and adsorbed molecules.
Yamada, Hidetaka; Murakami, Hiroshi; Shimada, Yukihiro
Hyomen Kagaku, 29(7), p.413 - 417, 2008/07
A femtosecond-laser-driven X-ray source and an X-ray focusing system have been developed for the time-resolved X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. The X-ray source, in which a plasma cathode induced by a 10 -W/cm
-W/cm laser pulse serves as an electron source of an X-ray tube, provides 10
laser pulse serves as an electron source of an X-ray tube, provides 10 Cu K
Cu K photons in 4
photons in 4 sr per pulse. The X-ray pulse duration is measured to be about two hundred nanoseconds. Emission analysis of the plasma cathode indicates that the temporal characteristics of the X-ray pulse are determined by the dynamics of the plasma particles under the electrostatic shielding against the applied voltage in the X-ray tube. As for the X-ray focusing system, a focal spot size by a polycapillary lens is measured and the enhancement of X-ray fluorescence intensity due to the lens is demonstrated.
sr per pulse. The X-ray pulse duration is measured to be about two hundred nanoseconds. Emission analysis of the plasma cathode indicates that the temporal characteristics of the X-ray pulse are determined by the dynamics of the plasma particles under the electrostatic shielding against the applied voltage in the X-ray tube. As for the X-ray focusing system, a focal spot size by a polycapillary lens is measured and the enhancement of X-ray fluorescence intensity due to the lens is demonstrated.
 2 single-domain surface
2 single-domain surfaceYamada, Yoichi; Girard, A.*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Shamoto, Shinichi
Hyomen Kagaku, 29(7), p.401 - 406, 2008/07
Widely well-defined Si(110)-16 2 single-domain surface has been fabricated utilizing the electromigration of the surface atoms. Tuning the direction of the dc during resistive heating to that of the surface reconstruction row realizes an alignment of the rows in one direction producing a mm-wide single-domain of 16
2 single-domain surface has been fabricated utilizing the electromigration of the surface atoms. Tuning the direction of the dc during resistive heating to that of the surface reconstruction row realizes an alignment of the rows in one direction producing a mm-wide single-domain of 16 2 structure. The fabricated single-domain shows number of useful characteristics such as a strong one-dimensionality and the surface homochirality, suggesting various applications.
2 structure. The fabricated single-domain shows number of useful characteristics such as a strong one-dimensionality and the surface homochirality, suggesting various applications.
 7 heteroepitaxial growth
7 heteroepitaxial growthAsaoka, Hidehito; Yamazaki, Tatsuya; Shamoto, Shinichi; Arnoldo, A.*; Goto, Seiichi*; Suemitsu, Maki*
Hyomen Kagaku, 28(9), p.500 - 503, 2007/09
Stress evolution during initial stage of Ge nanodot formation on Si(111)-7 7 has been investigated by using simultaneous measurements of the substrate curvature and the surface morphology. In the beginning of the first bilayer growth of Ge on Si(111)-7
7 has been investigated by using simultaneous measurements of the substrate curvature and the surface morphology. In the beginning of the first bilayer growth of Ge on Si(111)-7 7, a strong compressive film stress is observed, indicating a formation of a two-dimensional wetting layer. When the layer thickness approaches the critical one for three-dimensional nanodot nucleation, a clear bend in the stress curve is observed, corresponding to a partial relaxation of the lattice planes on the surface of the nanodots. Moreover, a stress transition has been also found to exist in the very early stage of the nanodot formation, which is concurrent with the trench formation around the three-dimensional nanodots.
7, a strong compressive film stress is observed, indicating a formation of a two-dimensional wetting layer. When the layer thickness approaches the critical one for three-dimensional nanodot nucleation, a clear bend in the stress curve is observed, corresponding to a partial relaxation of the lattice planes on the surface of the nanodots. Moreover, a stress transition has been also found to exist in the very early stage of the nanodot formation, which is concurrent with the trench formation around the three-dimensional nanodots.